Plastic injection molding is one of the most widely used manufacturing processes in the modern industrial world. From automotive components and medical devices to packaging products and consumer goods, injection molding enables manufacturers to produce high-quality, precision plastic parts at scale. Its ability to deliver consistent dimensional accuracy, fast production cycles, and cost efficiencies has made it the backbone of plastic manufacturing.
At LOG Injection Molding Machine, based in Fort Myers, FL, we provide advanced injection molding solutions designed to help businesses improve productivity, reduce waste, and deliver exceptional product quality. Whether you are scaling up production or exploring custom plastic part manufacturing, understanding how plastic injection molding works is critical to your success.
What is Plastic Injection Molding?
Plastic injection molding is a manufacturing process in which molten plastic is injected under high pressure into a precisely engineered mold cavity. Once the plastic cools and solidifies, the molded part takes the shape of the cavity and is ejected. This method is ideal for producing millions of identical parts with tight tolerances and consistent quality, making it a top choice across industries.
The process is used in producing a vast range of parts such as:
- Automotive interior and exterior components
- Consumer electronics housings
- Medical device components
- Food packaging and closures
- Industrial and household products
With advanced plastic injection molding machines from LOG Injection Molding Machine, manufacturers achieve reliable performance, optimized productivity, and superior surface finish on every part.
How Does Plastic Injection Molding Work? (Step-by-Step Breakdown)
Understanding the workflow of plastic injection molding helps manufacturers optimize design and production outcomes. The process consists of the following key stages:
1. Material Feeding
Plastic resin pellets are fed from a hopper into the injection molding machine. Common materials include ABS (Acrylonitrile Butadiene Styrene), polypropylene (PP), polyethylene (PE), nylon, and polycarbonate — each selected based on strength, flexibility, and application requirements.
2. Melting & Plasticizing
The pellets enter a heated barrel where a rotating screw generates heat through friction and external heaters. This transforms the plastic into a molten form with uniform viscosity. Precision temperature control is critical for quality outcomes.
3. Injection Into the Mold
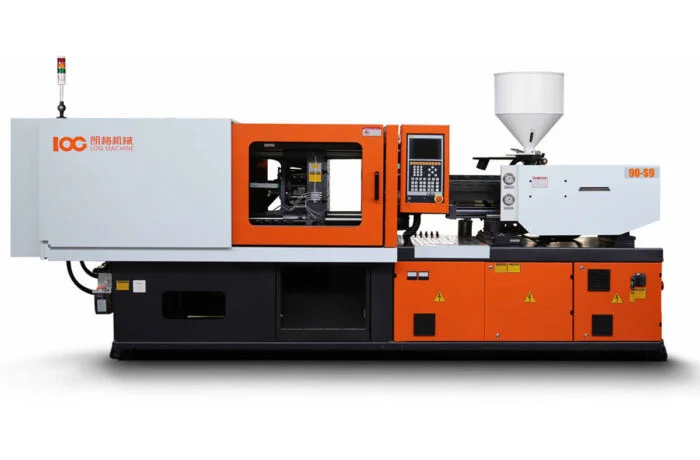
Once the material reaches the proper melt state, it is injected into the closed mold cavity under high pressure. This ensures complete filling, even for complex shapes and fine details. This step is powered by advanced machinery such as the LOG-S8 90 Ton Servo Injection Molding Machine — ideal for producing small to medium components with precision and efficiency.
4. Cooling and Solidification
After the molten plastic fills the cavity, it begins to cool and solidify. Cooling channels within the mold circulate coolant to manage temperature, reduce cycle times, and ensure dimensional stability.
5. Mold Opening and Part Ejection
Once the plastic has solidified, the mold opens and ejector pins push the finished part out of the cavity. The cycle then begins again, making injection molding ideal for high-volume production.
6. Post-Processing and Inspection
After ejection, parts may undergo additional operations such as trimming, surface finishing, assembly, or quality inspection to ensure they meet specifications.
This automated workflow delivers consistent quality, reduced labor costs, and high throughput, which are foundational for modern manufacturing operations.
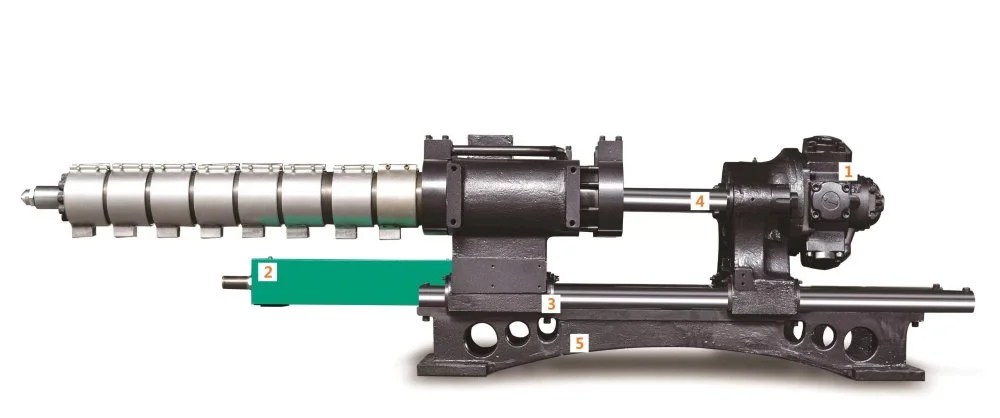
Main Components of an Injection Molding Machine
A plastic injection molding machine has several important subsystems that work together for precise and reliable production:
1. Injection Unit
The injection unit is responsible for melting plastic resin and injecting it into the mold. It consists of the hopper, barrel, reciprocating screw, heaters, and nozzle. Advanced units control pressure, temperature, and injection speed for optimal results.
2. Clamping Unit
The clamping unit holds the mold halves together under high pressure during injection and cooling. It includes:
- Clamping mechanism (hydraulic or electric)
- Tie bars and platens for alignment
- Mold opening and closing systems
Reliable clamping is critical for mold integrity and part accuracy.
3. Mold System
The mold itself determines the final shape of the part and includes:
- Cavity and core plates
- Runner and gate systems
- Cooling channels
- Ejector systems
A well-engineered mold reduces cycle time and improves part quality.
4. Drive Systems
Injection molding machines use either servo-hydraulic or electric drives. Servo drives offer precision motion control, energy savings, and smooth operation, making them ideal for modern manufacturing needs.
For example, the LOG-S8 400 Ton Servo Injection Molding Machine delivers robust clamping force, energy efficiency, and rapid production cycles — especially suited for medium to large part production.
5. Control System
A digital control system manages temperatures, pressures, timing, and cycle sequences. Intelligent controls help maintain consistent quality and reduce errors.
Injection Molding Machine Models by LOG
LOG Injection Molding Machine offers a variety of machines designed to suit different production demands and industry applications:
- LOG-S8 160 Ton Servo Injection Molding Machine – Designed for automotive interior parts, industrial components, and multi-cavity molds.
- LOG-S8 210 Ton Servo Injection Molding Machine – Best suited for medium-sized plastic components, appliance parts, and packaging solutions.
- LOG-S8 320 Ton Servo Injection Molding Machine – Engineered for large plastic parts, crates, containers, and thick-wall components.
- LOG-S8 400 Ton Servo Injection Molding Machine – Built for heavy-duty molding, automotive structural parts, and industrial enclosures.
These models feature energy-efficient servo-hydraulic systems, intelligent controls, and modular designs that minimize maintenance downtime and support flexible production requirements.
Why Plastic Injection Molding is Vital for Modern Manufacturing
Plastic injection molding offers manufacturers a range of powerful advantages:
- High production efficiency — ideal for large-scale manufacturing.
- Exceptional precision — for tight tolerances and consistent parts.
- Wide range of material compatibility — from commodity to engineered resins.
- Low cost per unit — especially for high volumes.
- Minimal material waste — often with recyclable regrind.
These benefits explain why injection molding remains the go-to production method for products in industries like automotive, electronics, medical devices, and consumer goods.
Conclusion
Plastic injection molding is a cornerstone of modern manufacturing — enabling high-quality, high-volume production with consistent precision. By understanding the working principles, main components, and workflow of injection molding machines, businesses can optimize design choices, production quality, and long-term costs.
At LOG Injection Molding Machine in Fort Myers, FL, we provide state-of-the-art machines and expert support designed to help manufacturers succeed today and tomorrow. Explore our lineup of servo injection molding machines to find equipment tailored to your production needs and efficiency goals.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
1. What materials can plastic injection molding use?
Common materials include PP, ABS, PE, nylon, and engineering resins — selected based on strength, temperature resistance, and application requirements.
2. Are servo injection molding machines more efficient?
Yes — servo systems reduce energy consumption, improve precision, and increase responsiveness compared with traditional hydraulic systems.
3. What tonnage should I choose for my part?
Machine tonnage depends on part size, projected area, and expected injection pressure — LOG’s team can help you select the right model.
4. Can LOG machines be used for automotive parts?
Yes — models like the LOG-S8 250 Ton and LOG-S8 400 Ton are ideal for automotive, packaging, and industrial components.
5. How does the LOG S-8 90 Ton model perform?
It offers precision, energy-efficient servo hydraulics, and fast cycle times — ideal for high-quality small to medium plastic parts.